Audiometric testing monitors an employee’s hearing, providing valuable insights into their auditory health and safeguarding their well-being in the workplace. This comprehensive evaluation plays a crucial role in detecting hearing loss early on, preventing potential complications, and ensuring a safe and productive work environment.
Audiometric testing encompasses a range of techniques and procedures designed to assess an individual’s hearing sensitivity and identify any abnormalities. By monitoring employee hearing over time, organizations can proactively address hearing loss, minimize its impact on workplace safety and productivity, and promote a healthy and supportive work environment.
Audiometric Testing Basics
Audiometric testing plays a crucial role in workplace hearing conservation programs. It evaluates an employee’s hearing sensitivity to detect any potential hearing loss or damage.
Types of Audiometric Tests
- Pure-Tone Audiometry: Measures hearing thresholds for specific frequencies.
- Speech Audiometry: Assesses speech recognition and comprehension abilities.
- Otoacoustic Emissions (OAE): Evaluates the function of the inner ear.
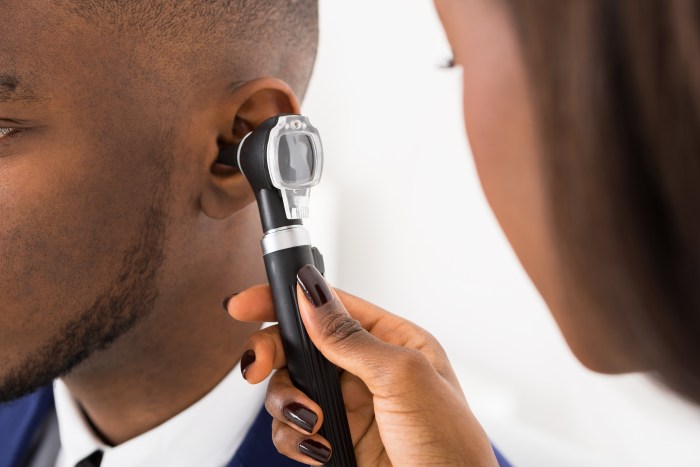
Procedure of Audiometric Testing
An audiometric test typically involves the following steps:
- Pre-test interview and explanation of the procedure.
- Insertion of headphones or earplugs for sound delivery.
- Presentation of sounds at varying frequencies and intensities.
- Employee’s indication of hearing or not hearing the sounds.
Monitoring Employee Hearing
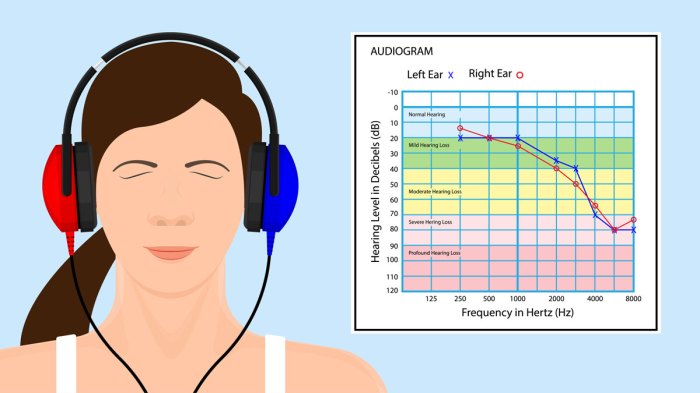
Regular audiometric testing is essential for monitoring employee hearing over time. It helps detect early signs of hearing loss, enabling prompt intervention and prevention of further damage.
Consequences of Untreated Hearing Loss
- Communication difficulties and misunderstandings.
- Reduced productivity and job performance.
- Increased risk of accidents and injuries.
- Social isolation and mental health concerns.
Audiometric Testing Methods
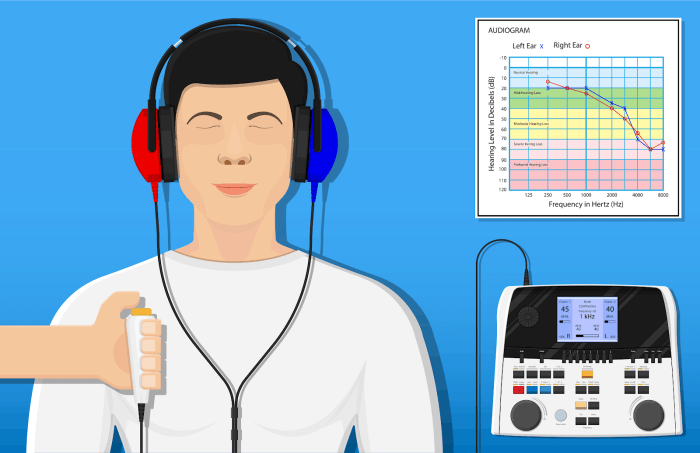
Various methods are employed in audiometric testing, each with its advantages and disadvantages.
Pure-Tone Audiometry
Pure-tone audiometry is the most common method, using pure tones to determine hearing thresholds. It is relatively simple and inexpensive.
Speech Audiometry
Speech audiometry assesses speech recognition and comprehension. It is useful for evaluating hearing loss that affects speech perception.
Otoacoustic Emissions (OAE)
OAE testing measures the sound produced by the inner ear in response to sound stimulation. It is often used to screen for hearing loss in newborns and infants.
Data Analysis and Interpretation
Audiometric test results are analyzed and interpreted to determine the presence and severity of hearing loss.
Criteria for Hearing Loss, Audiometric testing monitors an employee’s hearing
- Hearing Threshold Levels (HTLs): Thresholds at which sounds are barely audible.
- Speech Reception Threshold (SRT): Level at which speech can be understood 50% of the time.
Interpretation of Audiograms
Audiograms are graphical representations of hearing thresholds. They can identify patterns of hearing loss, such as:
- Conductive hearing loss: Caused by problems in the outer or middle ear.
- Sensorineural hearing loss: Damage to the inner ear or auditory nerve.
- Mixed hearing loss: A combination of conductive and sensorineural hearing loss.
Reporting and Follow-Up

Audiometric test results should be reported clearly and concisely to employees and management.
Reporting Process
- Provide a written report summarizing the test results.
- Explain any hearing loss detected and its potential impact.
- Recommend appropriate follow-up actions.
Follow-Up Procedures
- Medical referral for further evaluation or treatment.
- Hearing protection devices or assistive listening devices.
- Reassignment to a quieter work environment.
- Regular monitoring to track hearing status.
FAQ Summary: Audiometric Testing Monitors An Employee’s Hearing
What is the purpose of audiometric testing?
Audiometric testing aims to assess an individual’s hearing sensitivity and identify any hearing loss or abnormalities. It plays a vital role in monitoring employee hearing over time and detecting hearing loss early on.
How often should audiometric testing be conducted?
The frequency of audiometric testing depends on the specific work environment and exposure to noise. However, it is generally recommended that employees exposed to hazardous noise levels undergo audiometric testing annually or as required by regulatory standards.
What are the potential consequences of untreated hearing loss in the workplace?
Untreated hearing loss can have significant consequences in the workplace, including reduced productivity, increased risk of accidents, and difficulty communicating with colleagues. It can also lead to social isolation and reduced quality of life.