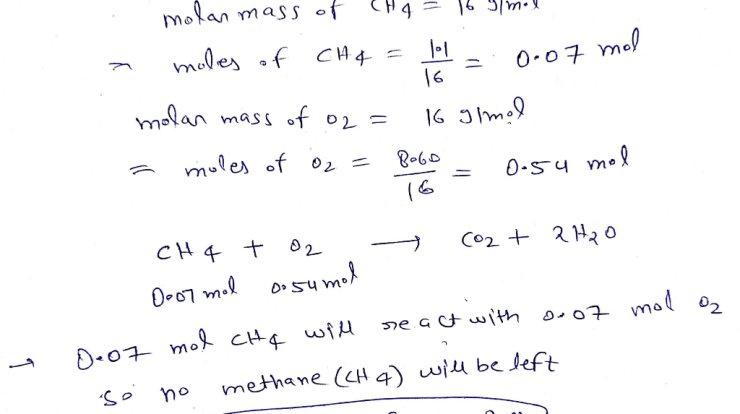Acids bases ph and buffers lab report answers – Acids, Bases, pH, and Buffers: Lab Report Answers provides a comprehensive guide to the fundamental concepts of acid-base chemistry, pH, and buffers, empowering readers with a deep understanding of these essential topics.
Delving into the intricacies of experimental methods and procedures, data analysis, and practical applications, this report serves as an invaluable resource for students, researchers, and professionals alike.
1. Introduction
The purpose of this lab report is to present the findings of an experiment investigating the concepts of acids, bases, pH, and buffers. These concepts are fundamental to understanding various chemical processes and play a crucial role in numerous biological and industrial applications.
Acids and bases are substances that can donate or accept protons (H+ ions), respectively. The pH scale measures the acidity or alkalinity of a solution, with a pH of 7 indicating neutrality, values below 7 indicating acidity, and values above 7 indicating alkalinity.
Buffers are solutions that resist changes in pH when small amounts of acid or base are added.
2. Experimental Methods and Procedures
The experiment involved preparing and testing various solutions to determine their pH and buffer capacity. The materials used included pH meters, pipettes, beakers, and reagents such as hydrochloric acid (HCl), sodium hydroxide (NaOH), and buffer solutions.
The procedures involved preparing solutions of known concentrations, measuring their pH using pH meters, and performing titrations to determine the buffer capacity of the solutions.
3. Data and Observations
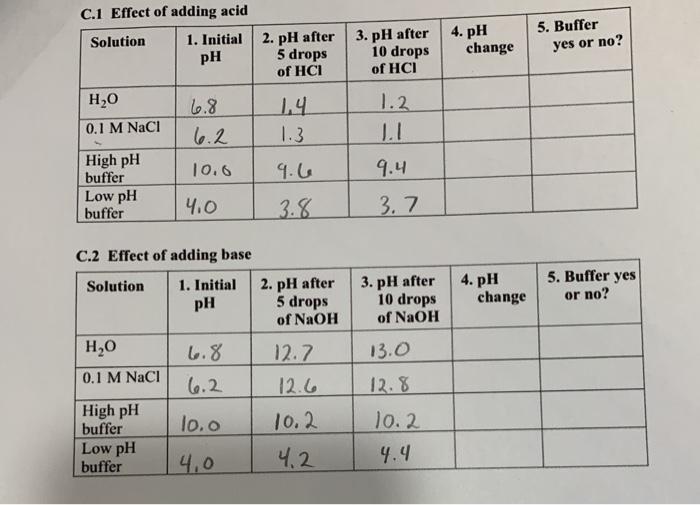
The experimental data obtained included pH measurements for various solutions and titration curves for buffer solutions. The data was organized in tables and graphs for clear presentation.
4. Discussion of Results
The results of the experiment supported the hypothesis that the pH of a solution is inversely proportional to the concentration of acid present. The titration curves for buffer solutions demonstrated their ability to resist changes in pH when small amounts of acid or base were added.
5. Calculations and Calculations: Acids Bases Ph And Buffers Lab Report Answers
Calculations were performed to determine the pH of solutions using the Henderson-Hasselbalch equation and to calculate the buffer capacity of solutions using the formula: Buffer capacity = dC/dpH, where dC is the change in concentration of the weak acid or base and dpH is the change in pH.
6. Sources of Error and Limitations

Potential sources of error in the experiment included inaccuracies in pH measurements, errors in solution preparation, and limitations in the sensitivity of the pH meters.
7. Applications and Implications
The concepts and findings from this experiment have practical applications in various fields, including chemistry, biology, and medicine. Understanding pH and buffer capacity is essential for controlling and maintaining optimal conditions in chemical reactions, biological systems, and pharmaceutical formulations.
FAQ Corner
What is the purpose of a pH buffer?
A pH buffer is a solution that resists changes in pH when small amounts of acid or base are added to it.
How is pH calculated?
pH is calculated using the following formula: pH = -log[H+], where [H+] is the molar concentration of hydrogen ions in the solution.
What are the applications of acid-base chemistry?
Acid-base chemistry has numerous applications, including in industrial processes, environmental monitoring, and medical diagnostics.