Navigating the body muscular system #3 – Navigating the body’s muscular system #3 embarks on an enthralling exploration of the human body’s intricate machinery, unveiling the remarkable interplay of muscles, movement, and control.
Delving into the complexities of muscle structure and function, this guide illuminates the fundamental principles that govern muscle contraction, relaxation, and coordination. By unraveling the intricate tapestry of muscle attachments and actions, we gain a profound appreciation for the body’s ability to execute a vast repertoire of movements.
Overview of the Muscular System
The muscular system is a complex network of tissues that plays a crucial role in human movement, posture, and overall physical function. It consists of specialized cells called muscle fibers that have the unique ability to contract and relax, enabling us to perform a wide range of voluntary and involuntary movements.
Structure and Function of Muscles
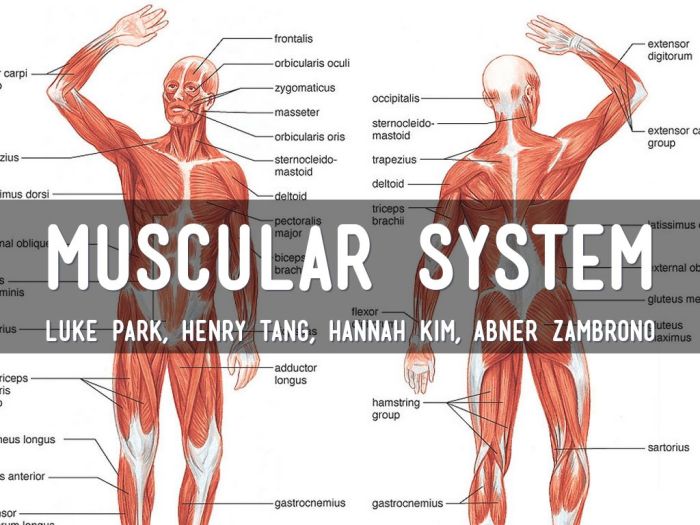
Muscles are composed of bundles of muscle fibers, which are further organized into smaller units called myofibrils. Each myofibril contains repeating units called sarcomeres, which are the basic contractile units of muscle tissue. Muscle contraction occurs through the sliding of actin and myosin filaments within the sarcomeres, resulting in shortening of the muscle fibers.
Types of Muscle Contractions, Navigating the body muscular system #3
- Isometric:Muscle tension increases without a change in muscle length.
- Isotonic:Muscle length changes while tension remains constant.
- Eccentric:Muscle lengthens while tension increases.
FAQ Guide: Navigating The Body Muscular System #3
What are the different types of muscle contractions?
There are three main types of muscle contractions: isometric, isotonic, and eccentric.
How do muscles attach to bones?
Muscles attach to bones through tendons, which are tough, fibrous connective tissues.
What is the role of motor units in muscle control?
Motor units are groups of muscle fibers that are innervated by a single motor neuron. They play a crucial role in muscle recruitment and control.