Which of the following statements are true concerning electromagnetic induction? This question delves into the fascinating realm of electromagnetic induction, a phenomenon that underpins countless technologies and applications in our modern world. From the fundamental principles discovered by Faraday and Lenz to the practical applications that shape our daily lives, this exploration unravels the intricacies of electromagnetic induction, revealing its significance and impact across diverse fields.
Electromagnetic induction, at its core, involves the generation of an electromotive force (EMF) or voltage across a conductor when it is subjected to a changing magnetic field. This phenomenon, governed by Faraday’s and Lenz’s laws, has revolutionized our understanding of electricity and magnetism, leading to groundbreaking advancements in power generation, electric motors, transformers, and a myriad of other devices.
Electromagnetic Induction
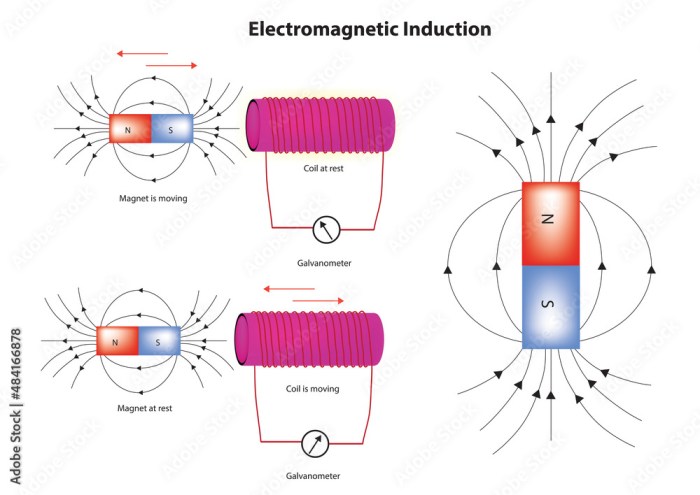
Electromagnetic induction is the production of an electromotive force (EMF) across an electrical conductor in response to a change in magnetic flux through the conductor. This phenomenon was discovered independently by Michael Faraday and Joseph Henry in 1831.Electromagnetic induction is the basis for many electrical devices, such as generators, transformers, and electric motors.
It is also used in a variety of applications, such as metal detectors, current sensors, and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) machines.
Faraday’s Law of Induction
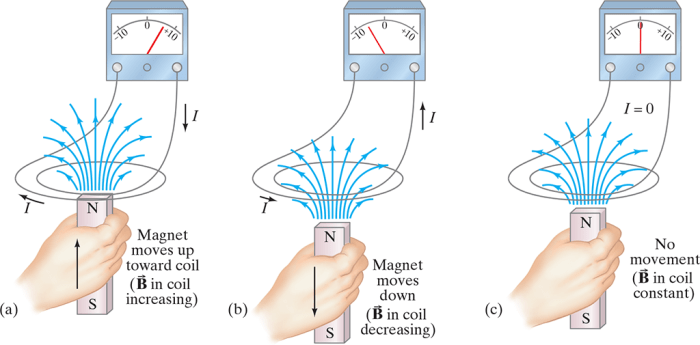
Faraday’s law of induction states that the electromotive force (EMF) induced in a conductor is equal to the negative of the rate of change of magnetic flux through the conductor. The mathematical equation for Faraday’s law is:“`EMF =
dΦ/dt
“`where:* EMF is the electromotive force in volts
- Φ is the magnetic flux in webers
- t is time in seconds
Lenz’s Law, Which of the following statements are true concerning electromagnetic induction
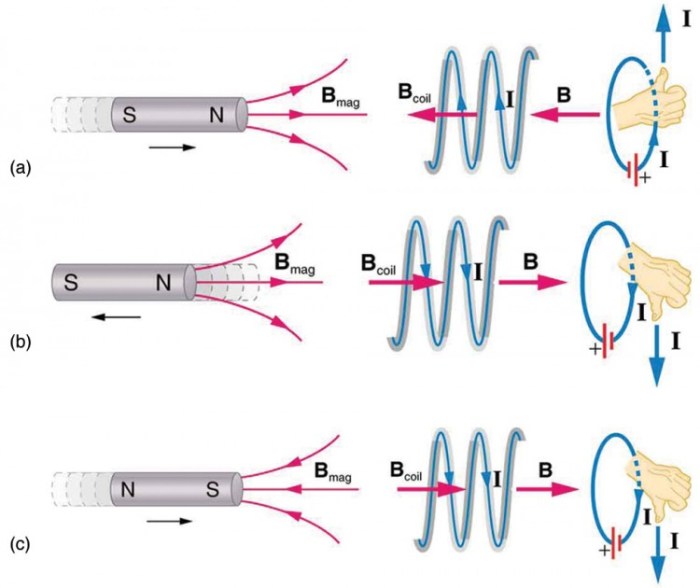
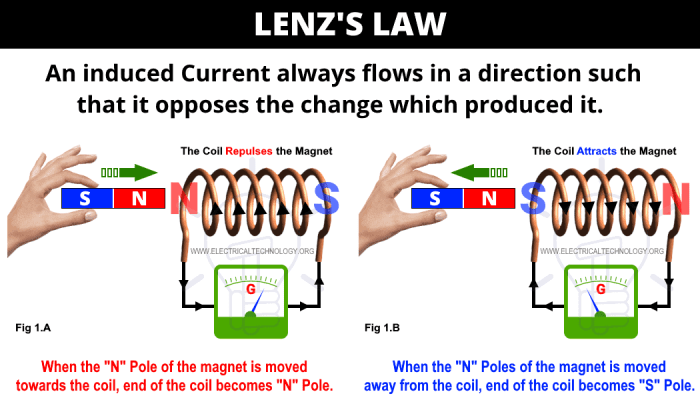
Lenz’s law is a consequence of Faraday’s law of induction. It states that the direction of the induced current in a conductor is such that it opposes the change in magnetic flux that produced it. This means that the induced current will flow in a direction that tends to keep the magnetic flux constant.Lenz’s
law can be used to determine the direction of the induced current in a conductor. The direction of the induced current is given by the right-hand rule. According to the right-hand rule, if you point your right thumb in the direction of the magnetic field and your fingers in the direction of the motion of the conductor, then your middle finger will point in the direction of the induced current.
Types of Electromagnetic Induction
There are two main types of electromagnetic induction:*
-*Static induction
This type of induction occurs when there is a change in the magnetic field around a conductor. The change in magnetic field can be caused by a moving magnet, a changing current in a nearby coil, or a change in the permeability of the material around the conductor.
-*Dynamic induction
This type of induction occurs when a conductor moves through a magnetic field. The motion of the conductor causes a change in the magnetic flux through the conductor, which in turn induces an EMF in the conductor.
Applications of Electromagnetic Induction
Electromagnetic induction is used in a wide variety of applications, including:*
-*Generators
Generators convert mechanical energy into electrical energy by using electromagnetic induction. When a conductor is rotated in a magnetic field, an EMF is induced in the conductor. This EMF can be used to power electrical devices.
-
-*Transformers
Transformers are used to change the voltage of an alternating current (AC) circuit. Transformers use electromagnetic induction to transfer energy from one circuit to another.
-*Electric motors
Electric motors convert electrical energy into mechanical energy by using electromagnetic induction. When an electric current flows through a conductor in a magnetic field, a force is exerted on the conductor. This force can be used to rotate a motor.
-*Metal detectors
Metal detectors use electromagnetic induction to detect the presence of metal objects. When a metal object is placed in a magnetic field, it creates a change in the magnetic field. This change in magnetic field can be detected by a metal detector.
-*Current sensors
Current sensors use electromagnetic induction to measure the current flowing through a conductor. When a current flows through a conductor, it creates a magnetic field. This magnetic field can be detected by a current sensor.
-*Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) machines
MRI machines use electromagnetic induction to create images of the inside of the human body. MRI machines use a strong magnetic field to align the protons in the body. When the magnetic field is turned off, the protons release energy that can be detected by the MRI machine.
This energy can be used to create images of the inside of the body.
FAQ Compilation: Which Of The Following Statements Are True Concerning Electromagnetic Induction
What is the fundamental principle behind electromagnetic induction?
Electromagnetic induction arises from the interaction between a changing magnetic field and a conductor, resulting in the generation of an electromotive force (EMF) across the conductor.
How does Faraday’s Law quantify electromagnetic induction?
Faraday’s Law mathematically expresses the relationship between the EMF induced in a conductor and the rate of change of magnetic flux through the conductor.
What is the significance of Lenz’s Law in electromagnetic induction?
Lenz’s Law determines the direction of the induced current in a conductor, opposing the change in magnetic flux that produced it.