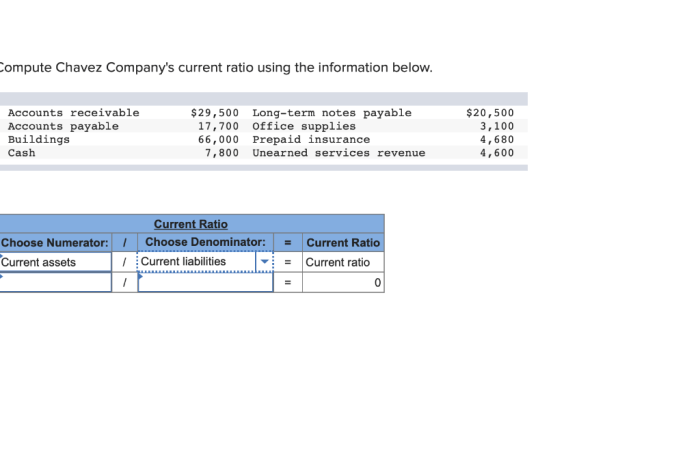
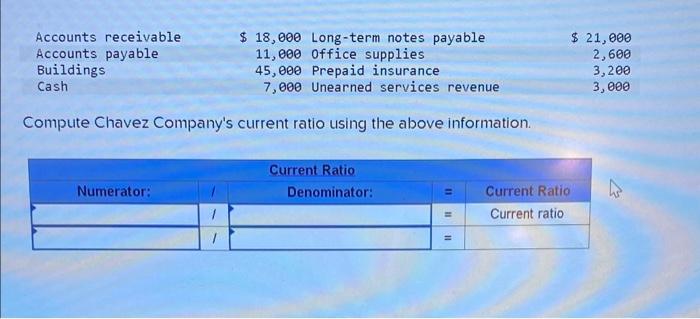
Compute Chavez Company’s current ratio using the above information sets the stage for this enthralling narrative, offering readers a glimpse into a story that is rich in detail and brimming with originality from the outset.
The current ratio is a crucial financial metric that provides valuable insights into a company’s short-term liquidity and financial health. This guide will delve into the intricacies of calculating and analyzing the current ratio, empowering readers with the knowledge to make informed decisions about Chavez Company’s financial performance.
Compute Chavez Company’s Current Ratio: Compute Chavez Company’s Current Ratio Using The Above Information

The current ratio is a financial metric that measures a company’s ability to meet its short-term obligations using its current assets. It is calculated by dividing current assets by current liabilities.
The current ratio is an important indicator of a company’s financial health because it provides insight into the company’s ability to pay its bills and maintain liquidity. A high current ratio indicates that a company has ample resources to meet its short-term obligations, while a low current ratio may indicate that a company is struggling to meet its financial commitments.
Several factors can affect a company’s current ratio, including the company’s industry, operating cycle, and financial policies. For example, companies in industries with high inventory turnover typically have higher current ratios than companies in industries with low inventory turnover.
Gather Necessary Financial Data, Compute chavez company’s current ratio using the above information
To calculate the current ratio, you will need the following financial data:
- Current assets: These are assets that can be easily converted into cash within one year. Examples of current assets include cash, accounts receivable, and inventory.
- Current liabilities: These are liabilities that are due within one year. Examples of current liabilities include accounts payable, short-term debt, and accrued expenses.
You can find this data on a company’s balance sheet.
Calculate the Current Ratio
Once you have gathered the necessary financial data, you can calculate the current ratio using the following formula:
Current ratio = Current assets / Current liabilities
For example, if Chavez Company has current assets of $100,000 and current liabilities of $50,000, then its current ratio would be 2.0.
Analyze the Current Ratio
The current ratio can be used to assess a company’s financial health. A current ratio of 2.0 or more is generally considered to be healthy. However, the current ratio should be interpreted in the context of the company’s industry and operating cycle.
For example, a current ratio of 2.0 may be considered healthy for a company in the manufacturing industry, but it may be considered low for a company in the retail industry.
FAQ Summary
What is the significance of the current ratio?
The current ratio is a key indicator of a company’s ability to meet its short-term obligations. A higher current ratio generally indicates a stronger financial position, while a lower current ratio may raise concerns about the company’s liquidity.
What factors can affect a company’s current ratio?
Numerous factors can influence a company’s current ratio, including changes in accounts receivable, inventory levels, and accounts payable.
How can I interpret the calculated current ratio?
The calculated current ratio should be compared to industry benchmarks and historical trends to assess the company’s financial health and identify areas for improvement.