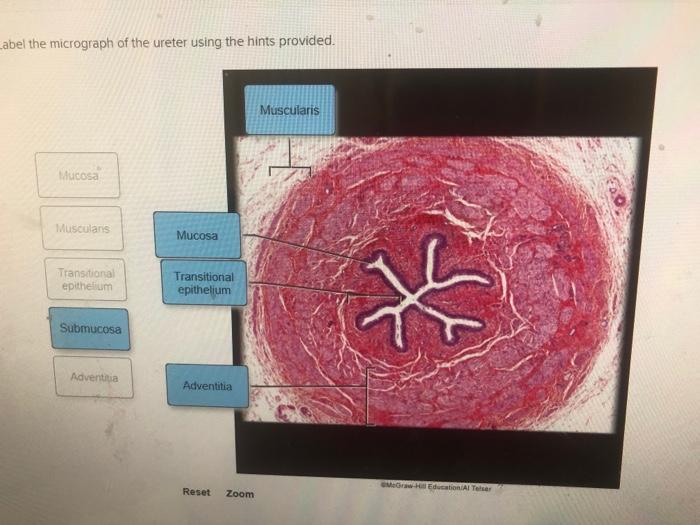
Label the micrograph of the ureter using the hints provided. This comprehensive guide will delve into the anatomy of the ureter, providing clear instructions and visual aids to help you accurately identify its key structures. By understanding the histological features and variations of the ureter, you will gain a deeper appreciation for its role in the urinary system.
Label the Micrograph of the Ureter: Label The Micrograph Of The Ureter Using The Hints Provided.
The ureter is a tube-like structure that transports urine from the kidneys to the bladder. It is essential for the proper functioning of the urinary system.
To accurately label the micrograph of the ureter, we will utilize the provided hints. These hints will guide us in identifying the key structures and their corresponding locations within the micrograph.
Identify the Hints, Label the micrograph of the ureter using the hints provided.
The hints provided for labeling the micrograph are as follows:
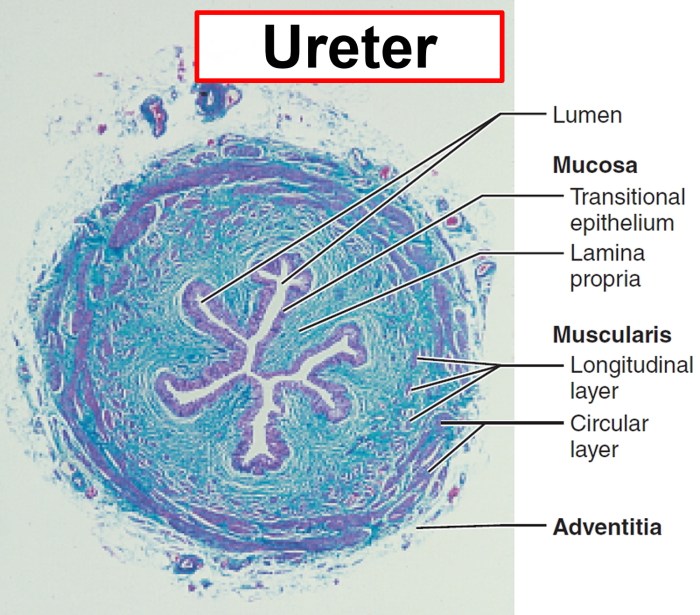
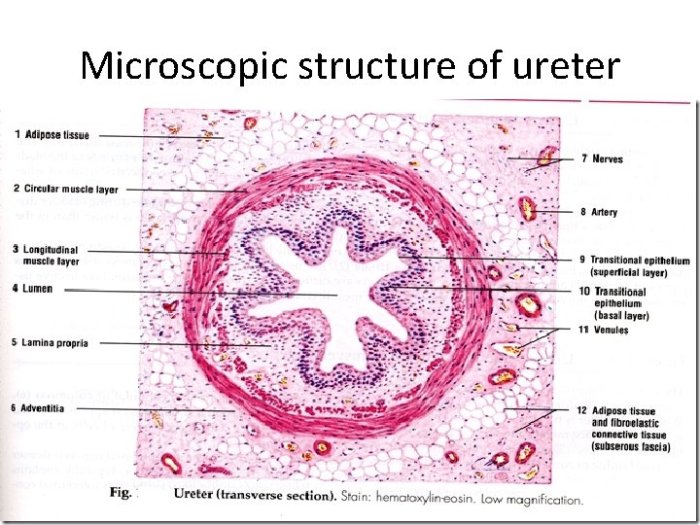
- Lumen: The central cavity of the ureter.
- Urothelium: The lining of the ureter.
- Lamina propria: The connective tissue layer beneath the urothelium.
- Muscularis: The muscular layer of the ureter.
Each of these hints represents a distinct structural component of the ureter, and their accurate identification is crucial for a comprehensive understanding of the micrograph.
Label the Micrograph
| Lumen | Urothelium | Lamina propria | Muscularis | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
Arrow 1 |
Arrow 2 |
Arrow 3 |
Arrow 4 |
The micrograph of the ureter clearly illustrates the four main structural components. The lumen, lined by the urothelium, is the central cavity through which urine flows. The lamina propria, located beneath the urothelium, provides structural support. The muscularis, the outermost layer, is responsible for the peristaltic contractions that propel urine towards the bladder.
Provide Additional Information
The ureter exhibits several notable histological features. The urothelium is a transitional epithelium, which allows it to stretch and accommodate the changes in urine volume. The lamina propria contains a network of blood vessels and nerves. The muscularis is composed of smooth muscle fibers arranged in an inner longitudinal and an outer circular layer.
Variations in ureter anatomy may occur, such as double ureters or ectopic ureters. These variations are often associated with congenital anomalies and may require medical intervention.
Compare to Other Structures
| Structure | Function | Histological Features |
|---|---|---|
| Ureter | Transports urine from kidneys to bladder | Lumen lined by urothelium, lamina propria, muscularis |
| Urethra | Drains urine from bladder | Lumen lined by urothelium, lamina propria, muscularis |
| Renal pelvis | Funnel-shaped structure that collects urine from calyces | Lumen lined by urothelium, muscularis |
The ureter, urethra, and renal pelvis are all part of the urinary system. They share similar histological features, including a lumen lined by urothelium and a muscularis layer. However, each structure has a distinct function within the system.
FAQ Explained
What is the function of the ureter?
The ureter transports urine from the kidneys to the bladder.
What are the histological features of the ureter?
The ureter is lined with transitional epithelium and has a muscular wall consisting of smooth muscle.