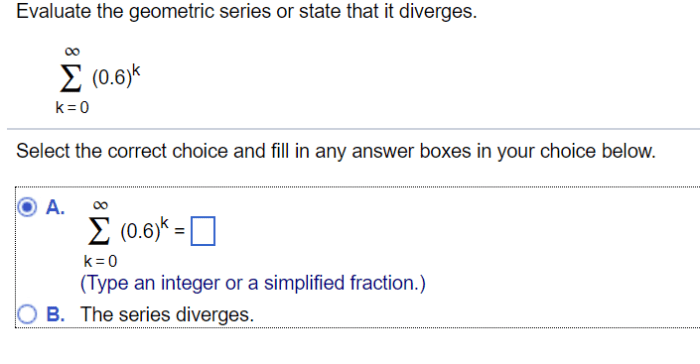
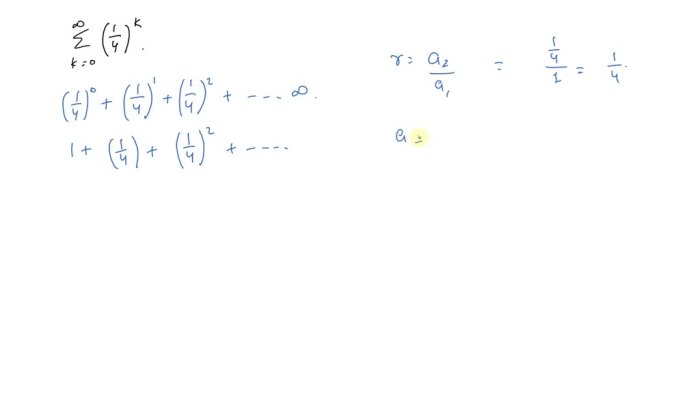Evaluate the geometric series or state that it diverges. – Geometric series, characterized by their common ratio, hold immense significance in mathematical analysis. This discourse delves into the intricacies of evaluating geometric series, exploring their convergence and divergence properties, with real-world applications and limitations.
Geometric series, represented as the sum of terms with a constant ratio between them, form the cornerstone of this discussion. Their evaluation relies on a specific formula, which we shall explore in detail, along with examples to solidify understanding.
Evaluating Geometric Series
A geometric series is an infinite sum of terms that have a common ratio between them. The common ratio is the ratio of any two consecutive terms in the series. For example, the series 2, 4, 8, 16, 32, … is a geometric series with a common ratio of 2. The formula for evaluating the sum of a finite geometric series is:
$$S_n = \fraca(1
- r^n)1
- r$$
where:* $S_n$ is the sum of the first $n$ terms of the series
- $a$ is the first term of the series
- $r$ is the common ratio of the series
- $n$ is the number of terms in the series
To apply the formula, simply substitute the values of $a$, $r$, and $n$ into the formula and evaluate. For example, to find the sum of the first 5 terms of the series 2, 4, 8, 16, 32, … we would use the formula:$$S_5 = \frac2(1
- 2^5)1
- 2 = \frac2(1
- 32)-1 = 62$$
Divergence of Geometric Series, Evaluate the geometric series or state that it diverges.
A geometric series diverges if the absolute value of the common ratio is greater than or equal to 1. For example, the series 1, 2, 4, 8, 16, … diverges because the absolute value of the common ratio is 2, which is greater than 1. When a geometric series diverges, the sum of the series is not defined.
FAQ Resource: Evaluate The Geometric Series Or State That It Diverges.
What is a geometric series?
A geometric series is an infinite sum of terms, each of which is obtained by multiplying the previous term by a constant ratio.
How do you evaluate a geometric series?
The sum of a finite geometric series is given by the formula S = a(1 – r^n) / (1 – r), where a is the first term, r is the common ratio, and n is the number of terms.
What is the difference between convergence and divergence?
Convergence refers to the situation where the sum of a series approaches a finite limit as the number of terms increases. Divergence occurs when the sum does not approach a finite limit.