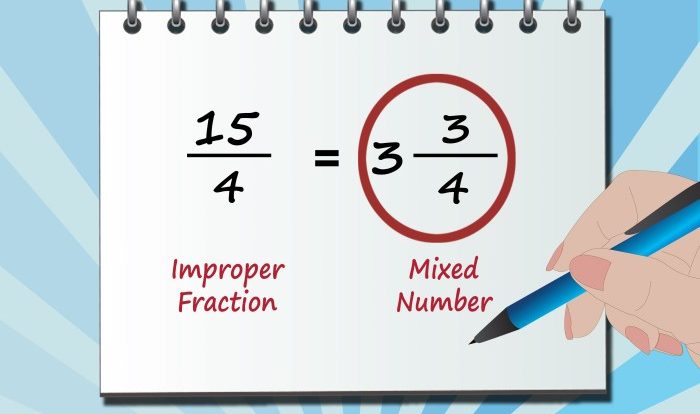
If the dimensions of a figure are multiplied by 5 – Exploring the intriguing concept of multiplying the dimensions of a figure by 5, this discourse delves into the profound effects it exerts on its geometric characteristics. By examining the changes in area, volume, perimeter, surface area, and scale, we uncover the intricate relationships that govern these properties.
This comprehensive analysis unveils the implications for real-world applications, ranging from architecture to engineering, where precise understanding of dimensional alterations is crucial for successful design and construction.
Dimension and Ratio Changes
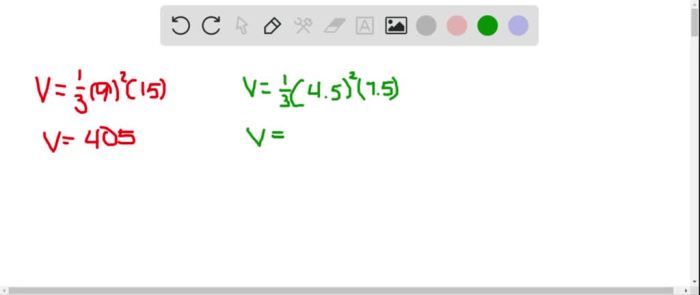
When all dimensions of a figure are multiplied by 5, the area of the figure is multiplied by 5 2, and the volume is multiplied by 5 3. This is because the area of a figure is proportional to the square of its dimensions, and the volume is proportional to the cube of its dimensions.
The ratios of different dimensions remain the same after the multiplication. For example, if the length of a rectangle is multiplied by 5 and the width is multiplied by 3, the ratio of the length to the width remains the same (5:3).
Perimeter and Surface Area Impact
The perimeter of a figure is the sum of the lengths of its sides. When all dimensions of a figure are multiplied by 5, the perimeter is multiplied by 5.
The surface area of a figure is the sum of the areas of its faces. When all dimensions of a figure are multiplied by 5, the surface area is multiplied by 5 2.
For example, if the length of a cube is multiplied by 5, the perimeter of the cube is multiplied by 5, and the surface area is multiplied by 5 2.
Volume and Capacity Transformations
The volume of a figure is the amount of space it occupies. When all dimensions of a figure are multiplied by 5, the volume is multiplied by 5 3.
The capacity of a figure is the amount of liquid or other substance it can hold. When all dimensions of a figure are multiplied by 5, the capacity is multiplied by 5 3.
For example, if the length of a cylinder is multiplied by 5, the volume of the cylinder is multiplied by 5 3, and the capacity of the cylinder is multiplied by 5 3.
Scale and Proportion Considerations
Scale is the ratio of the size of an object to the size of its representation. Proportion is the relationship between the sizes of different parts of an object.
When all dimensions of a figure are multiplied by 5, the scale of the figure is multiplied by 5. The proportions of the figure remain the same.
For example, if a model of a car is scaled up by a factor of 5, the model is 5 times larger than the actual car, but the proportions of the model are the same as the proportions of the actual car.
Real-World Applications, If the dimensions of a figure are multiplied by 5
The multiplication of dimensions by 5 is relevant in a variety of real-world scenarios, including:
- Architecture: When designing buildings, architects often use scale models to represent the actual buildings. The dimensions of the scale models are typically multiplied by a factor of 5 or 10 to make them easier to work with.
- Engineering: Engineers use scale models to test the performance of new designs. The dimensions of the scale models are often multiplied by a factor of 5 or 10 to make them easier to test.
- Manufacturing: Manufacturers use scale models to create prototypes of new products. The dimensions of the scale models are often multiplied by a factor of 5 or 10 to make them easier to manufacture.
FAQ Insights: If The Dimensions Of A Figure Are Multiplied By 5
What happens to the area of a figure when its dimensions are multiplied by 5?
The area is multiplied by 25 (5 squared).
How does multiplying dimensions affect the volume of a figure?
The volume is multiplied by 125 (5 cubed).
What is the impact on the perimeter of a figure when its dimensions are multiplied by 5?
The perimeter is multiplied by 5.
How does scale factor relate to multiplying dimensions?
The scale factor is 5 when dimensions are multiplied by 5.