Contrasting mitosis and meiosis answer key – Contrasting Mitosis and Meiosis: A Comprehensive Answer Key introduces a detailed exploration of the fundamental differences between mitosis and meiosis, providing a comprehensive understanding of these crucial cellular processes.
This in-depth analysis delves into the distinct characteristics, significance, and implications of mitosis and meiosis, shedding light on their roles in cell division and genetic diversity.
1. Define Mitosis and Meiosis
Define Mitosis
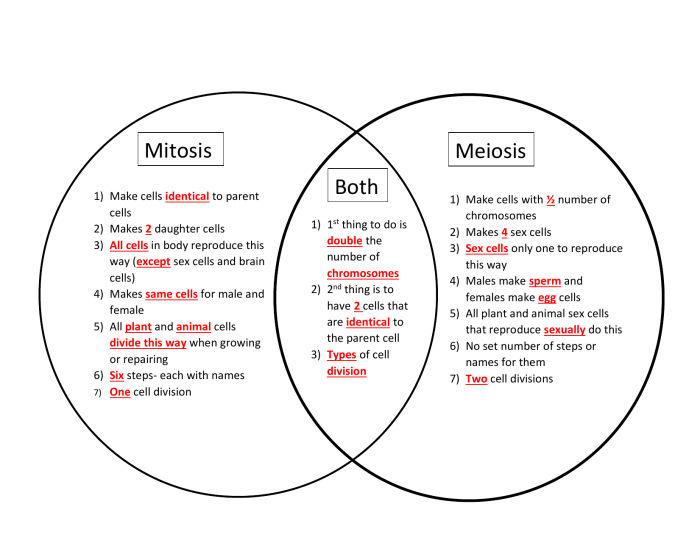
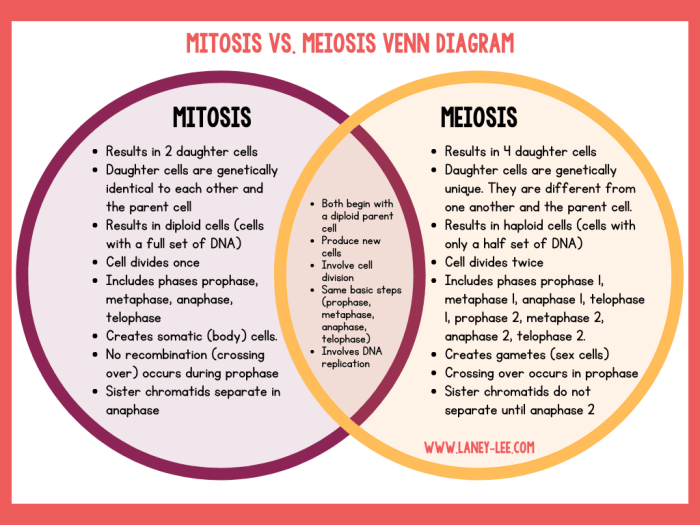
Mitosis is a type of cell division that results in two daughter cells that are genetically identical to the parent cell. It is a continuous process that occurs in somatic cells (non-sex cells) and is essential for growth, repair, and asexual reproduction.
Define Meiosis
Meiosis is a type of cell division that results in four daughter cells that have half the number of chromosomes as the parent cell. It is a discontinuous process that occurs in germ cells (sex cells) and is essential for sexual reproduction.
2. Compare the Number of Cell Divisions
Number of Cell Divisions in Mitosis
Mitosis consists of one round of cell division, resulting in two daughter cells.
Number of Cell Divisions in Meiosis
Meiosis consists of two rounds of cell division, resulting in four daughter cells.
3. Contrast the Number of Daughter Cells
Number of Daughter Cells in Mitosis
Mitosis produces two daughter cells.
Number of Daughter Cells in Meiosis
Meiosis produces four daughter cells.
4. Describe the Chromosome Number: Contrasting Mitosis And Meiosis Answer Key
Chromosome Number in Mitosis
The daughter cells of mitosis have the same number of chromosomes as the parent cell (diploid number, 2n).
Chromosome Number in Meiosis
The daughter cells of meiosis have half the number of chromosomes as the parent cell (haploid number, n).
5. Elaborate on Synapsis and Crossing Over
Synapsis and Crossing Over
During meiosis, homologous chromosomes pair up during a process called synapsis. During this process, genetic material is exchanged between the homologous chromosomes through a process called crossing over. This genetic recombination results in the production of daughter cells with new combinations of genetic material, increasing genetic diversity.
6. Create a Table Summarizing Key Differences
Table of Key Differences between Mitosis and Meiosis, Contrasting mitosis and meiosis answer key
| Process | Number of Cell Divisions | Number of Daughter Cells | Chromosome Number | Purpose |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mitosis | 1 | 2 | Diploid (2n) | Growth, repair, asexual reproduction |
| Meiosis | 2 | 4 | Haploid (n) | Sexual reproduction |
Q&A
What is the primary purpose of mitosis?
Mitosis is responsible for cell growth, tissue repair, and asexual reproduction.
How does meiosis contribute to genetic diversity?
Meiosis involves crossing over and independent assortment of chromosomes, resulting in the production of genetically diverse gametes.
What is the key difference in the number of daughter cells produced by mitosis and meiosis?
Mitosis produces two identical daughter cells, while meiosis produces four genetically distinct daughter cells.