Welcome to the realm of APUSH Unit 4, where the winds of change swept through the nascent United States. As you embark on this historical odyssey with our apush unit 4 study guide pdf, we invite you to immerse yourself in the transformative events and ideas that shaped a nation’s destiny.
This comprehensive guide will serve as your trusty compass, navigating you through the complexities of Unit 4. From the era of revolution to the crucible of civil war, we’ll explore the key concepts, pivotal figures, and enduring themes that defined this pivotal chapter in American history.
APUSH Unit 4 Overview
APUSH Unit 4 covers the period from 1754 to 1800, a time of significant change and upheaval in American history. This era witnessed the outbreak of the French and Indian War, the American Revolution, and the formation of the United States.
Key themes of Unit 4 include:
- The growing tensions between Britain and its American colonies
- The impact of the Enlightenment on American political thought
- The role of slavery in the development of the United States
- The challenges of creating a new nation
Key Concepts and Ideas
Unit 4 of APUSH explores the transformation of the United States from a rural, agricultural society to an urban, industrial powerhouse. Key concepts and ideas covered in this unit include:
• Industrialization: The rapid growth of factories, railroads, and other industries during the late 19th century.
• Urbanization: The movement of people from rural areas to cities, leading to the growth of large urban centers.
• Immigration: The influx of millions of immigrants from Europe and Asia, who provided labor for industries and helped shape American culture.
• Labor Unions: Organizations formed by workers to improve their working conditions and wages.
• Social Reform: Movements to address social problems such as poverty, child labor, and discrimination.
Significance of Industrialization
Industrialization transformed the American economy and society. It led to the rise of new industries, the growth of cities, and the creation of a new working class. Industrialization also had a significant impact on the environment, as factories polluted the air and water.
Significance of Urbanization
Urbanization led to the growth of large cities, which became centers of commerce, culture, and innovation. However, urbanization also brought challenges, such as overcrowding, poverty, and crime.
Significance of Immigration
Immigration helped to fuel the growth of American industries and cities. Immigrants also brought new cultures and ideas to the United States, which helped to shape American society.
Significance of Labor Unions
Labor unions played a key role in improving the working conditions and wages of American workers. Unions also helped to promote social reform and political change.
Significance of Social Reform
Social reform movements helped to address some of the social problems that emerged during the late 19th century. These movements led to the passage of laws that protected workers, children, and the environment.
Important People and Events
Unit 4 of APUSH covers a transformative period in American history, marked by westward expansion, industrialization, and social reform. Various individuals and events played pivotal roles in shaping the course of this era.
Key People
- Andrew Jackson: Seventh President of the United States, known for his populist policies, including the Indian Removal Act and the Bank War.
- William Henry Harrison: Ninth President of the United States, who died of pneumonia just 31 days after taking office.
- John Tyler: Tenth President of the United States, who succeeded Harrison after his death and vetoed the recharter of the Second Bank of the United States.
- James K. Polk: Eleventh President of the United States, who oversaw the annexation of Texas and the Mexican-American War.
- Zachary Taylor: Twelfth President of the United States, who died of cholera 16 months after taking office.
- Millard Fillmore: Thirteenth President of the United States, who succeeded Taylor after his death and signed the Compromise of 1850.
- Franklin Pierce: Fourteenth President of the United States, who supported the Kansas-Nebraska Act and the Gadsden Purchase.
- James Buchanan: Fifteenth President of the United States, who failed to prevent the secession of Southern states and the outbreak of the Civil War.
Key Events
- Indian Removal Act (1830): Legislation that forced Native American tribes to relocate west of the Mississippi River.
- Bank War (1832-1836): A political conflict between President Andrew Jackson and the Second Bank of the United States, resulting in the bank’s closure.
- Annexation of Texas (1845): The incorporation of the Republic of Texas into the United States, which contributed to the outbreak of the Mexican-American War.
- Mexican-American War (1846-1848): A conflict between the United States and Mexico over the annexation of Texas, resulting in the United States’ acquisition of vast territories in the Southwest.
- Compromise of 1850: A series of laws passed by Congress to resolve tensions between the North and South over the issue of slavery in the newly acquired territories.
- Kansas-Nebraska Act (1854): Legislation that repealed the Missouri Compromise and allowed slavery to be decided by popular sovereignty in the territories of Kansas and Nebraska.
- Dred Scott v. Sandford (1857): A Supreme Court ruling that denied citizenship to African Americans and declared the Missouri Compromise unconstitutional.
- Lincoln-Douglas Debates (1858): A series of debates between Abraham Lincoln and Stephen Douglas over the issue of slavery in the territories.
Documents and Sources: Apush Unit 4 Study Guide Pdf
Primary and secondary sources play a crucial role in understanding the events and ideas of Unit 4. These documents provide valuable insights into the perspectives, motivations, and experiences of individuals and groups during this transformative period.
Here are some important documents and sources related to Unit 4:
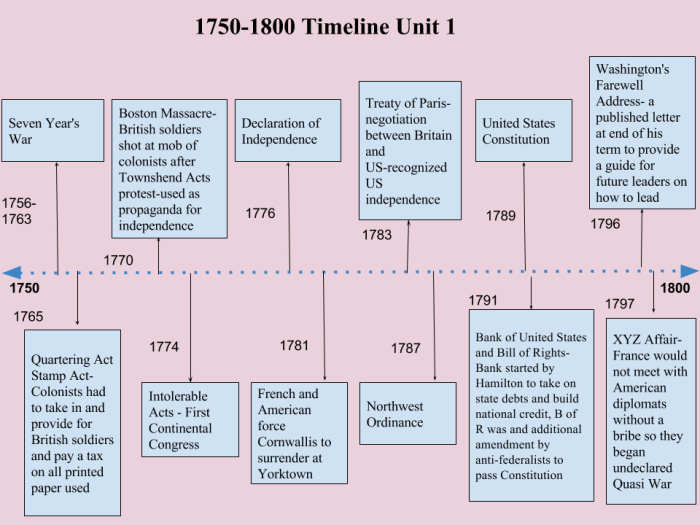
The Declaration of Independence
The Declaration of Independence, adopted on July 4, 1776, was a pivotal document that proclaimed the American colonies’ independence from British rule. It articulated the principles of natural rights, self-government, and the consent of the governed, shaping the foundation of American democracy.
I’ve been digging into the APUSH Unit 4 study guide PDF, but I’m getting distracted by this worm on a hook crossword . It’s so tricky! But I’m determined to ace this unit, so back to the study guide I go.
The Constitution of the United States
Ratified in 1788, the Constitution established the framework for the federal government and Artikeld the rights and responsibilities of citizens. It reflected the ideals of limited government, separation of powers, and checks and balances, ensuring a balance of authority among different branches of government.
The Federalist Papers
A series of 85 essays written by Alexander Hamilton, James Madison, and John Jay, the Federalist Papers advocated for the ratification of the Constitution. They provided a detailed analysis of the proposed government, its structure, and its implications for the nation.
The Bill of Rights
The Bill of Rights, ratified in 1791, consists of the first ten amendments to the Constitution. It guarantees fundamental rights and freedoms, such as freedom of speech, religion, and assembly, protecting individual liberties against government encroachment.
Letters from a Farmer in Pennsylvania
Written by John Dickinson in 1767-1768, these letters argued against the Townshend Acts, a series of taxes imposed by the British Parliament on the colonies. They emphasized the rights of colonists and the need for colonial self-government, influencing public opinion in the lead-up to the American Revolution.
Common Sense
Published by Thomas Paine in 1776, Common Sense was a pamphlet that advocated for American independence and criticized British rule. Its simple language and persuasive arguments resonated with the colonists, helping to mobilize support for the cause of independence.
Key Themes and Patterns
Unit 4 explores the transformation of the United States from a collection of colonies to an independent nation. Key themes and patterns emerge, shaping the nation’s identity and its role in the world.
These themes and patterns connect to the broader historical narrative by providing insights into the fundamental forces that have shaped American society and culture. They help us understand the challenges and triumphs that the nation has faced, and how these have influenced its development.
Patterns of Unity and Division
The American Revolution was a period of both unity and division. The colonies united to fight for independence, but they also struggled with internal conflicts over slavery, religious freedom, and economic interests. These patterns of unity and division would continue to shape the nation’s history.
The Impact of the Revolution
The American Revolution had a profound impact on the United States. It created a new nation based on the principles of liberty and equality. It also led to the development of a new political system and a new economic order.
The Expansion of the United States
In the years after the Revolution, the United States expanded rapidly. This expansion was driven by a combination of factors, including the desire for land, the need for resources, and the desire to spread American values.
The Development of American Culture, Apush unit 4 study guide pdf
The American Revolution also led to the development of a distinct American culture. This culture was influenced by a variety of factors, including the Enlightenment, the Protestant Reformation, and the experiences of the American people.
Practice Questions and Activities
Sharpen your understanding of Unit 4 concepts through a series of practice questions and engaging activities designed to reinforce your learning.
These exercises will challenge you to analyze primary sources, connect events to broader historical themes, and evaluate the impact of key figures and ideas.
Practice Questions
- Explain the significance of the Missouri Compromise in the context of westward expansion and the balance of power between free and slave states.
- Analyze the causes and consequences of the War of 1812, considering its impact on the United States’ foreign policy and national identity.
- Compare and contrast the economic and social systems of the North and South during the antebellum period, highlighting the factors that contributed to their distinct characteristics.
Engaging Activities
- Conduct a mock debate on the issue of slavery, with students taking on the perspectives of abolitionists, slaveholders, and politicians.
- Create a timeline of key events leading up to the Civil War, highlighting the pivotal decisions and turning points that shaped the conflict.
- Develop a research project on a specific figure or event from Unit 4, presenting your findings in a multimedia format such as a podcast or video essay.
Additional Resources
In addition to the materials provided in this study guide, here are some additional resources that you can explore to gain a deeper understanding of Unit 4:
Books
- The American Yawpby Joseph Ellis
- A Patriot’s History of the United Statesby Larry Schweikart and Michael Allen
- The Oxford History of the United Statesby Michael Beschloss
Websites
- The Gilder Lehrman Institute of American History: https://www.gilderlehrman.org/
- The National Archives: https://www.archives.gov/
- The Library of Congress: https://www.loc.gov/
Other Materials
- Documentaries on the American Revolution, such as “The American Revolution” by PBS
- Historical fiction novels set during the American Revolution, such as “Johnny Tremain” by Esther Forbes
- Primary source documents from the American Revolution, such as the Declaration of Independence and the Constitution
FAQ
Where can I find additional resources beyond the apush unit 4 study guide pdf?
Our guide includes a curated list of books, websites, and other materials to supplement your learning.
How do I effectively use the practice questions and activities in the guide?
Engage with the practice questions to test your understanding of key concepts. Utilize the activities to reinforce your learning through interactive exercises.